-
Shopping Tools
-
Care & Maintenance
-
About
-
Dealer Login
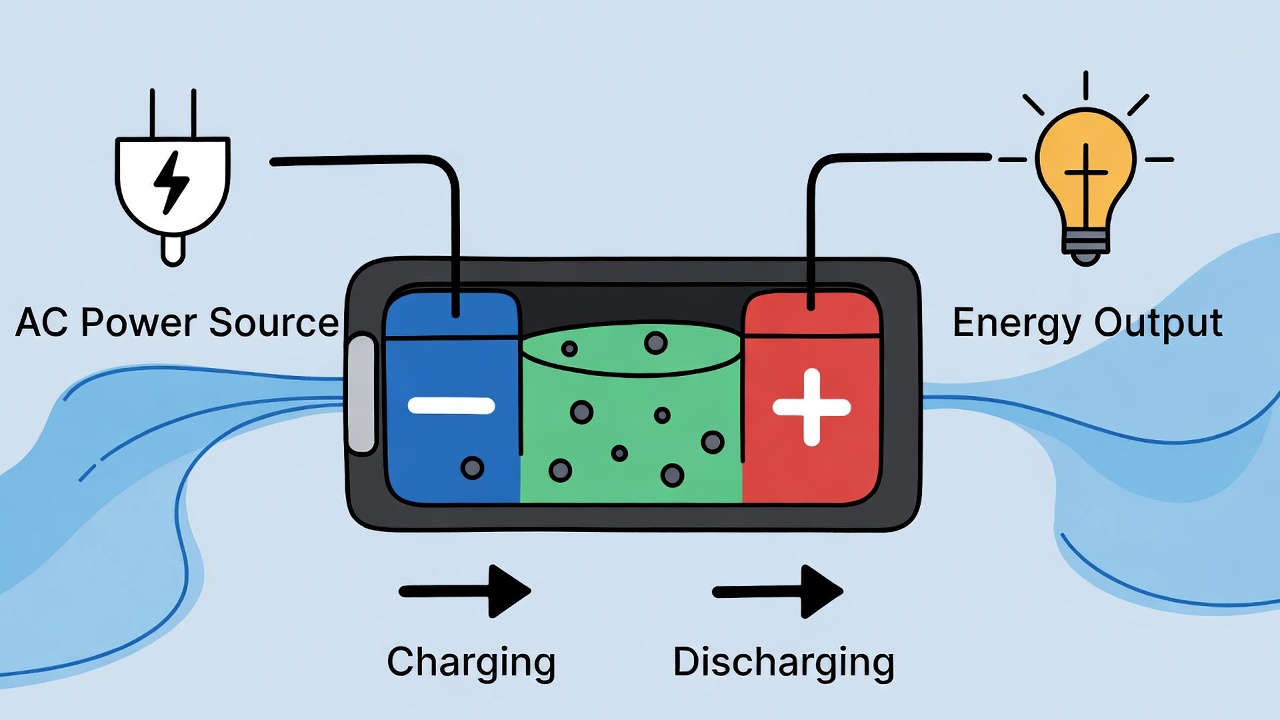
Lithium-ion batteries operate through a clever exchange of lithium ions between anode and cathode, facilitated by an electrolyte and separator – this reversible flow generates electricity while offering exceptional energy storage in a compact form.
Since their widespread adoption, lithium-ion batteries have become essential, delivering reliable power with minimal weight. Their unique chemistry sets them apart from traditional options, enabling longer runtime and faster recharges.
Every lithium-ion cell contains four primary parts:
External current collectors connect to circuits, completing the design.
During charging, an external source drives lithium ions from cathode through electrolyte to anode, where they embed in graphite. Electrons travel externally, creating potential.
When discharging (powering a device), ions move back to cathode, releasing electrons through the circuit to generate current. This "rocking chair" mechanism ensures reversibility and efficiency.
Modern battery management systems monitor voltage, temperature, and balance for optimal performance and safety.
These batteries excel with:
The primary drawback involves safety risks from thermal runaway – a chain reaction of overheating that can lead to fire or explosion if cells are damaged, overcharged, or exposed to extreme conditions. Built-in protections help, but incidents remain a concern.
Other challenges include higher initial cost, gradual capacity fade over time, and reliance on scarce materials like cobalt, driving ongoing research into safer, more sustainable alternatives.
Lithium-ion technology appears virtually everywhere:
In recreational applications, many modern electric golf carts now use lithium-ion packs, benefiting from lighter weight, longer lifespan, and consistent power delivery across full rounds without voltage drop.
Understanding lithium-ion battery operation reveals why they've transformed energy storage – balancing impressive performance with careful engineering to manage inherent risks. Continued advancements promise even broader, safer applications ahead.
